Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
Tags
- 빅데이터분석
- max
- 히스토그램 그리기
- 그래프시각화
- Sum
- 여러 데이터 검색
- Intersect
- 막대그래프
- count
- %in%
- 정보획득량
- loop 문
- 데이터분석가
- 총과 카드만들기
- 그래프 생성 문법
- 순위출력
- 회귀분석 알고리즘
- sqld
- 팀스파르타
- 빅데이터
- 회귀분석
- 불순도제거
- 데이터분석
- difftime
- merge
- 상관관계
- if문 작성법
- Dense_Rank
- 단순회귀 분석
- sql
Archives
- Today
- Total
ch0nny_log
[빅데이터분석] R _ 69. 모델 평가 본문









■ 실제 머신러닝 모델에서 정확도와 카파 통계량 출력하기
actual_type <- wbcd_test_label #테스트 데이터의 실제값 predict_type <- result1 #테스트 데이터의 예측값 positive_value <- 'Maliganant' # 관심범주(yes) negative_value <- 'Benign'# 관심범주(no) #■ 정확도 library(gmodels) g <-CrossTable( actual_type, predict_type ) x <- sum(g$prop.tbl *diag(2)) #정확도 확인하는 코드 x #0.9122807 #■ 카파통계량 install.packages("vcd") library(vcd) table(actual_type,predict_type) Kappa(table(actual_type, predict_type)) #0.8224 #■ 민감도 #install.packages("caret") library(caret) sensitivity(predict_type, actual_type, positive=positive_value) #0.8148148 #■ 특이도 specificity(predict_type, actual_type, negative=negative_value) #1 #■ 정밀도 posPredValue(predict_type, actual_type, positive=positive_value) #1 #■ 재현율 sensitivity( predict_type, actual_type, positive=positive_value) #0.8148148 #■ F1 score 구하기 library(MLmetrics) F1_Score( actual_type, predict_type, positive = positive_value) #0.8979592중요도: TP > TN > FP > FN


-> 민감도가 1에 가깝게 높은게 좋음 ( 환자입장에서 얼마나 잘 예측했는지)


-> 의사입장(모델입장) 에서 얼마나 잘 예측했는지


-> ( 의사입장에서 얼마나 잘 예측했는지)


-> 민감도와 같음 & 환자입장에서 얼마나 잘 예측했는자
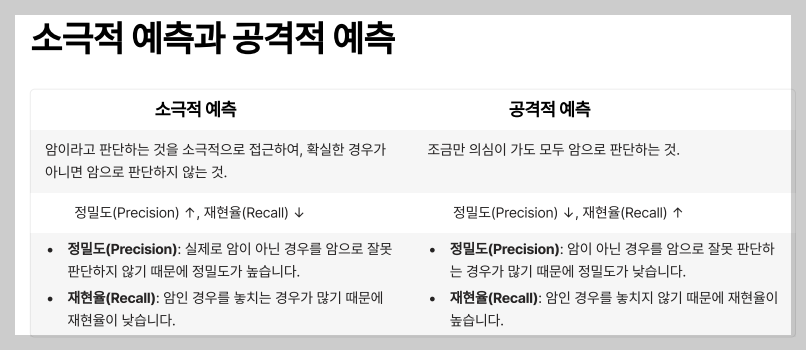
정확도가 100%인 모델은 현실에 없음




#1. 데이터 불러오기
setwd("c:\\data")
wbcd <- read.csv("wisc_bc_data.csv", header=T, stringsAsFactors=FALSE)
# 2. 종속변수를 팩터로 변환하기
wbcd$diagnosis <- factor( wbcd$diagnosis,
levels= c("B","M"),
labels=c("Benign", "Maliganant") )
str(wbcd)
nrow(wbcd) #569
#2. sample 함수를 이용해서 데이터를 섞습니다.
set.seed(2)
sample(10) # 1부터 10까지의 숫자를 랜덤으로 섞어서 출력하는 코드
wbcd_shuffle <- wbcd[ sample(569), ] # 설명: wbcd[ 행, 열 ]
wbcd_shuffle
#3. 최대 최소 정규화
wbcd2 <- wbcd_shuffle[ , -1 ] #id삭제
str(wbcd2)
normalize <- function(x) {
return ( (x-min(x)) / ( max(x) - min(x) ) )
}
wbcd_n <- as.data.frame( lapply( wbcd2[ , 2:31], normalize) )
nrow( wbcd_n ) # 569
#4. 훈련 데이터와 테스트 데이터를 9대 1로 분리합니다.
train_num <- round( 0.9 * nrow(wbcd_n), 0 ) #데이터를 9:1로 나눈다
train_num # 512
wbcd_train <- wbcd_n[ 1:train_num, ] # 훈련 데이터 구성
wbcd_test <- wbcd_n[ (train_num+1) : nrow(wbcd_n), ] # 테스트 데이터 구성
nrow(wbcd_test) # 57
wbcd_train_label <- wbcd2[ 1:train_num, 1 ] # 훈련 데이터의 정답
wbcd_test_label <- wbcd2[ (train_num+1) : nrow(wbcd_n), 1 ] # 테스트 데이터 정답
wbcd_test_label
#5. knn 모델을 생성합니다.
# install.packages("class")
library(class)
result1 <- knn(train=wbcd_train, test=wbcd_test, cl=wbcd_train_label, k=21)
result1
data.frame( result1, wbcd_test_label)
sum( result1 == wbcd_test_label ) #52
x <- data.frame('실제'=wbcd_test_label, '예측'=result1)
table(x)
actual_type <- wbcd_test_label #테스트 데이터의 실제값
predict_type <- result1 #테스트 데이터의 예측값
positive_value <- 'Maliganant' # 관심범주(yes)
negative_value <- 'Benign'# 관심범주(no)
#■ 정확도
library(gmodels)
g <-CrossTable( actual_type, predict_type )
x <- sum(g$prop.tbl *diag(2)) #정확도 확인하는 코드
x #0.9122807
#■ 카파통계량
install.packages("vcd")
library(vcd)
table(actual_type,predict_type)
Kappa(table(actual_type, predict_type)) #0.8224
#■ 민감도
#install.packages("caret")
library(caret)
sensitivity(predict_type, actual_type, positive=positive_value) #0.8148148
#■ 특이도
specificity(predict_type, actual_type, negative=negative_value) #1
#■ 정밀도
posPredValue(predict_type, actual_type, positive=positive_value) #1
#■ 재현율
sensitivity( predict_type, actual_type, positive=positive_value) #0.8148148
#■ F1 score 구하기
library(MLmetrics)
F1_Score( actual_type, predict_type, positive = positive_value) #0.8979592■ 성능척도 구현 문제.(독버섯 나이브 베이즈 모델 코드를 하나로 총정리 )
# ■독버섯 나이브 베이즈 모델 코드를 하나로 총정리 #1. 데이터 불러오기 mush <- read.csv("c:\\data\\mushrooms.csv", stringsAsFactors=TRUE) #2. 데이터 관찰하기 dim(mush) str(mush) #3. 훈련과 테스트 분할하기 library(caret) set.seed(1) k <- createDataPartition( mush$type, p=0.8, list=F) # 훈련 데이터 80% train_data <- mush[ k, ] test_data <- mush[ -k, ] #4. 모델 훈련하기 library(e1071) model <- naiveBayes( type ~ . , data=train_data, laplace=0.0001 ) #5. 테스트 데이터 예측하기 result <- predict( model, test_data[ , -1] ) # 정답 빼고 넣어줍니다. #6. 모델 평가하기 library(gmodels) sum(result == test_data[ , 1] ) / length( test_data[ , 1 ]) * 100 CrossTable(x=result, y=test_data[ , 1], chisq=TRUE ) #■다른 성능 척도 구하기 actual_type <- test_data[ , 1] #테스트 데이터의 실제값 predict_type <- result #테스트 데이터의 예측값 positive_value <- 'poisonous' # 관심범주(yes) negative_value <- 'edible' # 관심범주(no) #■ 정확도 library(gmodels) g <- CrossTable( actual_type, predict_type ) x <- sum(g$prop.tbl *diag(2)) #정확도 확인하는 코드 x #■ 카파통계량 install.packages("vcd") library(vcd) table(actual_type,predict_type) Kappa(table(actual_type, predict_type)) #■ 민감도 #install.packages("caret") library(caret) sensitivity(predict_type, actual_type, positive=positive_value) #■ 특이도 specificity(predict_type, actual_type, negative=negative_value) #■ 정밀도 posPredValue(predict_type, actual_type, positive=positive_value) #■ 재현율 sensitivity( predict_type, actual_type, positive=positive_value) #■ F1 score 구하기 library(MLmetrics) F1_Score( actual_type, predict_type, positive = positive_value)
정확도 카파통계량 민감도 특이도 정밀도 재현율 F1score laplace = 0.0001 0.9950739 Unweighted 0.9901/
weighted 0.99010.9923372 0.9976219 0.9974326 0.9923372 0.9948784
마지막문제. 독일 은행 데이터로 머신러닝 모델을 생성하는데 정확도 외에 위와 같이 다른 성능 척도도 같이 구해서 위와 같이 표로 정리하시오 !
데이터: credit.csv 총정리※ laplace 값을 변경해도 성능 척도 값이 일치함
정확도 카파통계량 민감도 특이도 정밀도 재현율 F1score laplace = 0.0001 0.695 0.2413 0.4166 0.8142 0.4901 0.4166 0.4504 laplace = 0.0002 0.695 0.2413 0.4166 0.8142 0.4901 0.4166 0.4504 laplace = 0.0003 0.695 0.2413 0.4166 0.8142 0.4901 0.4166 0.4504
'빅데이터 분석(with 아이티윌) > R' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [빅데이터분석] R _ 71. k-foldout (0) | 2024.07.30 |
|---|---|
| [빅데이터분석] R _ 70. ROC 커브와 cut-off (0) | 2024.07.30 |
| [빅데이터분석] R _ 68. K-means 알고리즘 (0) | 2024.07.26 |
| [빅데이터분석] R _ 67. 연관 분석 (0) | 2024.07.25 |
| [빅데이터분석] R _ 66. 신경망 (6) | 2024.07.24 |









